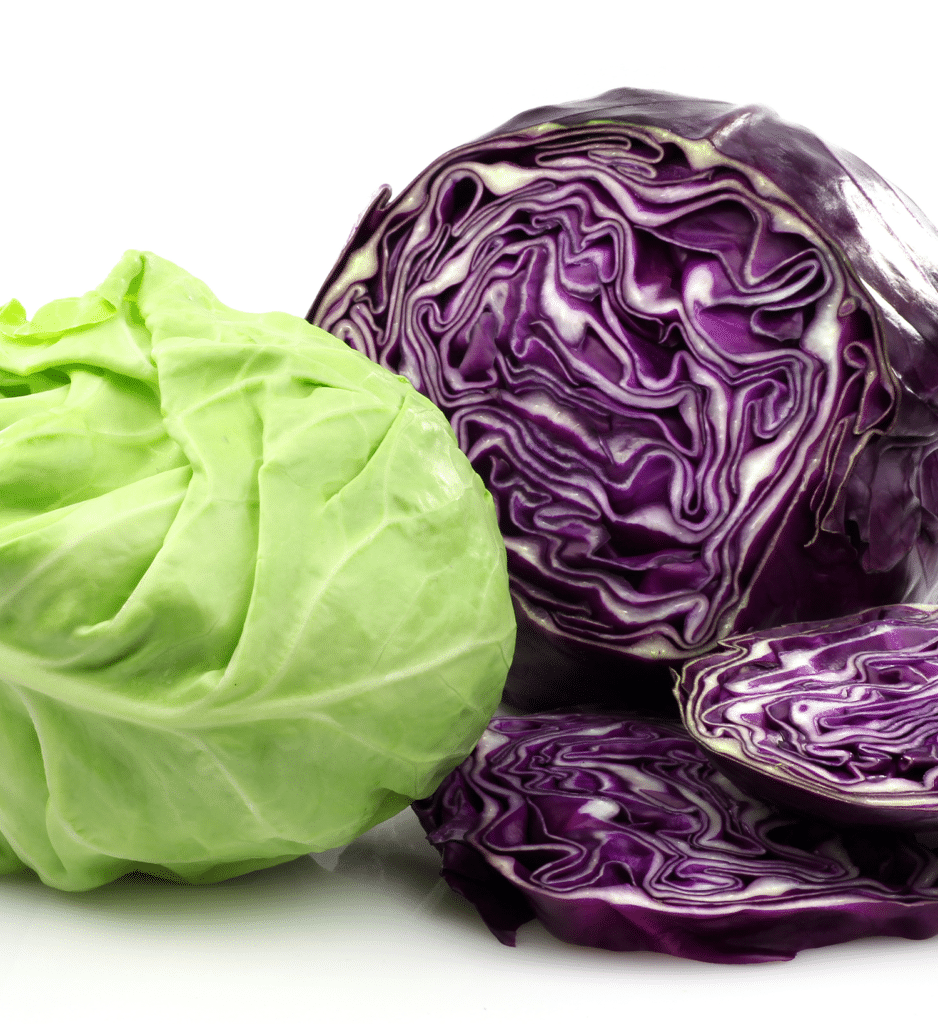
Cabbage
Testing has indicated the NNA cabbage is not only very strong in vitamins and minerals but also has a clean taste. With the red being sweeter than the white however both being very tasty..
According to various experts, Cabbage is rich in vitamin B6 and folate, which are essential for the immune and nervous system.
In addition, cabbage is high in fibre and contains powerful antioxidants,
Cabbage is especially high in vitamin C, a potent antioxidant that may protect against heart disease, certain cancers, and vision loss.
- Harvest Location: Western Australia
What is the difference between white and red cabbage?
Red Cabbage has amazing nutrients called phytonutrients which are supported by the nature occurring sulphur in the cabbage.
This enables the nutrients to flow very easily into the liver, making red cabbage a food must for rejuvenating the liver.
Red cabbage is used most often for healthy side dishes, salads and white/green cabbage in more cooked foods such as main courses and dishes.
Green cabbage is the vitamin K champion
Red cabbage is also loaded with vitamin K, although it does not beat the green cabbage, the vitamin K champion. According to USDA’s Nutrition Facts data, 1 ounce of raw red cabbage provides your body with about 13% of the Daily Value for vitamin K. By way of comparison, eating just one ounce of green cabbage will supply your body with a whopping 27% of the Daily Value for vitamin K.
Vitamin K is best known for its role in blood coagulation, but emerging research suggests it may also be one of the best vitamins for cardiovascular health and bone health: Vitamin K helps direct calcium into the bone, thereby reducing the risk of calcium build-up in blood vessels.
One cup of raw, chopped cabbage (89g) provides 22 calories, 1.1g of protein, 5.2g of carbohydrates, and 0.1g of fat. Cabbage also provides potassium, folate, and vitamin K. This nutrition information is provided by the USDA.1
- Calories: 22
- Fat: 0.1g
- Sodium: 16mg
- Carbohydrates: 5.2g
- Fiber: 2.2g
- Sugars: 2.9g
- Protein: 1.1g
- Potassium: 151mg
- Folate: 38.3mcg
- Vitamin K: 67.6mcg
Cabbage is best stored whole and unrinsed until you’re ready to use it. Cutting into it will cause it to lose vitamin C, which will lead to faster spoilage.
To store a head of cabbage, place it in a plastic bag in the crisper drawer of your fridge. A head of cabbage will last up two months when stored this way.